The Windows operating system was first introduced by Microsoft in November 1985, and Windows 1.0 was its initial release. Because MS-DOS was the preeminent operating system at the time, this version of Windows was created to serve as a GUI shell for it. Windows 1.0 was a piece of software that ran on top of MS-DOS rather than a full operating system.
A new method of using computers was one of the biggest changes that Windows 1.0 brought about. Users could now interact with the computer using a mouse and a graphical interface rather than having to type commands into the command line. Windows 1.0 offered a brand-new, easier-to-use interface for using computers, which contributed significantly to its popularity.
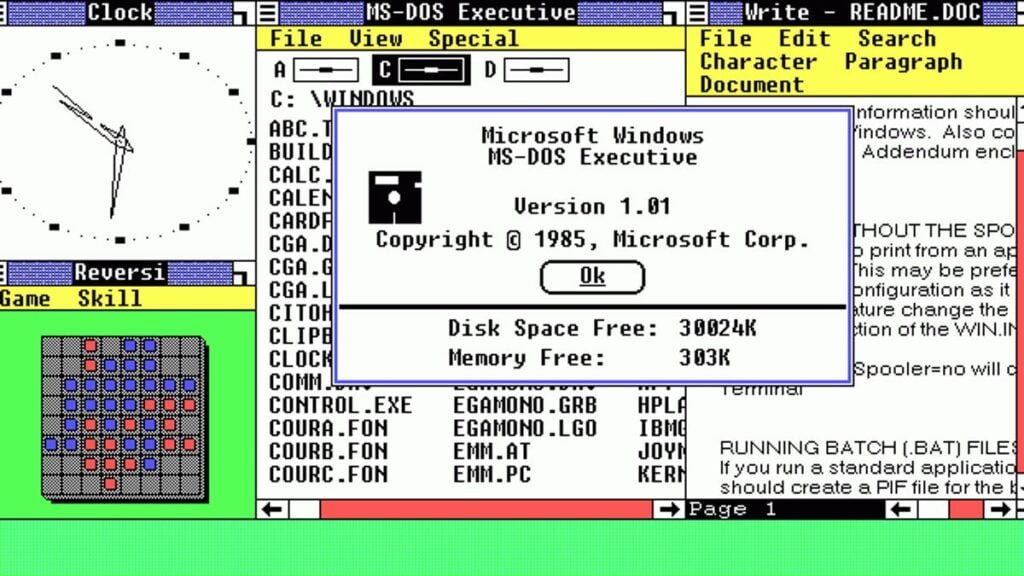
Numerous fundamental programs, including Calculator, Calendar, Clipboard Viewer, Notepad, Paint, and Write, were included in Windows 1.0’s initial release. Computers that are IBM PC compatible and have at least 256 KB of memory can use the software. 16-color graphics were also supported by Windows 1.0, which was a significant advancement over earlier computer systems.
The inability of Windows 1.0 to run multiple applications at once was one of its biggest drawbacks. Users had to close the current application in order to open a new one because they could only run one application at once. This was a significant drawback, especially for users who needed to use several applications at once.
System requirements
The official system requirements for Windows 1.0 include the following.
| Windows 1.01 | Windows 1.03 | Windows 1.04 | |
|---|---|---|---|
| CPU | 8088 processor | 8088 processor | 8088 processor |
| RAM | 256 KB of memory | 320 KB of memory | 320 KB of memory |
| Storage (for all versions) | Two double-sided floppy disk drives or a hard disk | ||
| Video | CGA, HGC, or EGA adapters | CGA, HGC, or EGA adapters | CGA, HGC, EGA, or VGA adapters |
| OS | MS-DOS 2.0 | MS-DOS 2.0 or higher | MS-DOS 2.0 or higher |
| Mouse (for all versions) | A Microsoft-compatible pointing device is recommended, but not required |
Besides the minimum system requirements, Microsoft has also published a note in which it recommended additional memory when using multiple applications or DOS 3.3.
Windows 1.0 was a significant turning point in the evolution of personal computer operating systems, despite its flaws. It offered a novel, user-friendly method of using computers and set the stage for later iterations of Windows. Additionally, Windows 1.0 contributed to Microsoft’s rise to prominence in the personal computer software industry.
Overall, the development of Microsoft’s Windows operating system began with Windows 1.0, which was a significant first step. It introduced a new method of using computers and paved the way for later iterations of Windows, which eventually took over as the most popular operating system for desktop computers.






