On May 22, 1990, Microsoft released Windows 3.0, the third iteration of their popular operating system. In comparison to earlier Windows versions, it represented a significant improvement in both performance and user interface. A number of new additions and upgrades made in Windows 3.0 laid the groundwork for later iterations of the operating system.
The addition of a new graphical user interface known as the Program Manager was one of Windows 3.0’s most important changes. Users now have an easier way to manage and launch applications, as well as organize their files, thanks to this new interface. The older File Manager, introduced with Windows 2.0, was replaced by the Program Manager.
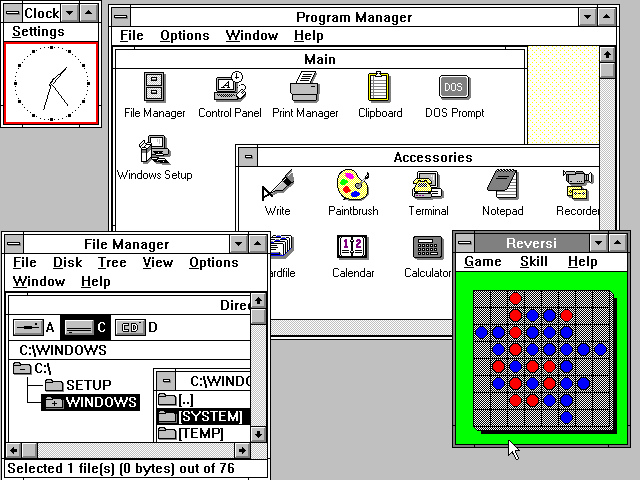
Virtual memory support, which allowed the operating system to use disk space to simulate more RAM, was another significant feature of Windows 3.0. This enhanced performance and stability while enabling users to run multiple applications simultaneously.
Windows 3.0 also introduced new application programming interfaces (APIs) that empowered developers to produce more complex and potent applications. This included improved networking capabilities, support for TrueType fonts, and improved graphics capabilities.
| Windows 3.0 | Windows 3.0 with Multimedia Extensions | |
|---|---|---|
| CPU | 8086/8088 processor or better | 80286 processor running at 10 MHz or better |
| RAM | 1 MB of memory (640 KB and 384 KB of conventional and extended memory, respectively) | 2 MB of memory |
| Storage | Hard drive with 6–8 MB of free space | Hard drive with 30 MB of total space |
| Medium | At least one floppy drive for the installation disks | A CD-ROM drive is essential for performing numerous multimedia operations. |
| Video | Windows 3.0 supports a large array of graphics cards and computer monitors and will try to use one of its generic drivers in the event that no driver exists to support the hardware. However, because the user interface is designed to be displayed at resolutions relatively high by 1990s standards, an EGA, MCGA, or VGA display was recommended. | VGA graphics card or better |
| OS | MS- or PC DOS version 3.1 or higher | |
| Mouse | A Microsoft-compatible pointing device is recommended. | A mouse is required to perform many multimedia operations. |
In conclusion, Microsoft and the Windows operating system both benefited greatly from the release of Windows 3.0. It unveiled a new graphical user interface, support for virtual memory, and new developer APIs. These upgrades laid the groundwork for later iterations of Windows as well as the creation of more sophisticated and feature-rich operating systems.